Many men seeking hair regrowth solutions turn to topical finasteride as a more localized treatment option than oral medications.
However, not all are aware of the potential side effects this treatment can cause.
This article explores the most commonly reported topical finasteride side effects so that you can make an informed decision about whether this hair loss treatment method is right for you.
Table of content
What is topical Finasteride?
Topical Finasteride is a medication applied directly to the scalp to treat male pattern baldness, specifically designed to treat it with fewer systemic impacts. It works by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone responsible for hair follicle shrinkage.
Diving a bit deeper, it's essentially the same drug as its oral counterpart but designed for those who prefer a localized approach to minimize systemic side effects.
This topical formulation aims to provide the benefits of Finasteride gel without the full-body impact, offering a promising option for individuals seeking to regrow hair loss, with potentially fewer side effects.
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
Does topical finasteride work?
Yes, topical Finasteride, often used alongside Finasteride Minoxidil, has been shown to be effective in promoting the natural hair growth cycle and reducing hair loss in individuals suffering from male androgenetic alopecia. Its targeted approach allows the medication to act directly on the scalp, where it's needed most.
When we get into the nitty-gritty, studies and user experiences suggest that topical Finasteride can be just as effective as the oral version for some, especially when it comes to increasing hair density and slowing down hair loss.
The advantage of topical Finasteride solutions is their application method, which focuses the drug's action on the hair follicles while aiming to limit serum DHT levels by minimizing its absorption into the bloodstream.
This localized treatment method has caught the eye of many looking for solutions to male pattern hair loss treatments, promising results without some of the systemic side effects associated with its oral counterpart.
What are the side effects of topical Finasteride?

Here are the side effects of topical Finasteride:
- Scalp irritation
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Sexual dysfunction
- Breast tenderness
- Allergic reactions
- Psychological effects
- Eye-related issues
Scalp irritation
The most frequently reported issue is scalp irritation. Users might notice redness, itching, and a burning sensation. This is usually the body's response to the new substance on the scalp and often diminishes over time.
Headache
A small number of individuals have reported experiencing headaches after using topical Finasteride. The exact cause isn't clear, but monitoring the frequency and severity is recommended.
Dizziness
Though less common, some users have felt dizzy after applying the medication. This could be related to the body adjusting to changes in DHT levels.
Sexual dysfunction
Even though topical application minimizes systemic absorption, instances of decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, side effects commonly associated with taking oral Finasteride, have been reported, albeit presumably at a lower incidence.
Breast tenderness
Gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissue in men, has been observed in rare cases, indicating a systemic effect of the medication despite its topical application.
Allergic reactions
Though uncommon, allergic reactions like skin rash, itching, and even shortness of breath can occur. Swelling in the face, eyelids, hands, or feet might also be a sign of a severe allergic reaction.
Psychological effects
A very small percentage of users report psychological side effects such as depression. It's crucial to monitor mental health closely while on treatment.
Eye-related issues
Some individuals have experienced dryness and vision changes, although these are relatively rare side effects.
It's important to remember that while topical Finasteride can lower DHT levels in the blood, its localized application aims to minimize systemic absorption. However, because it still affects DHT levels, being vigilant about side effects is key, especially for those sensitive to hormone fluctuations.
Topical finasteride vs oral finasteride
Topical Finasteride provides a targeted treatment for hair loss and hair growth with potentially fewer systemic side effects compared to oral Finasteride. While both the oral Finasteride treatment and the topical variant work by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to DHT, the hormone linked to androgenetic alopecia, the first topical finasteride formulation minimizes the drug's absorption into the bloodstream, potentially reducing side effects.
The decision between topical Finasteride and oral Finasteride treatments often hinges on weighing their effectiveness in hair regrowth against the profile of potential side effects, including erectile dysfunction and impact on male pattern hair growth and loss and hair follicles.
Oral Finasteride has a long track record of successfully treating hair loss but is known for its potential sexual side effects, among others, due to systemic absorption
Topical Finasteride, on the other hand, is designed to concentrate its action on the scalp, where it's needed, which may lessen the risk of systemic side effects like sexual dysfunction, depression, and breast tissue enlargement
However, it's important to note that while topical application reduces the likelihood of these side effects, it doesn't eliminate the risk entirely.
Individuals considering either form of Finasteride, whether prescription medication or topical Finasteride solutions, should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss their specific situation related to male androgenetic alopecia.
Who can use topical Finasteride?
Topical Finasteride is primarily aimed at men dealing with male and female pattern baldness both, as this condition is linked to DHT levels. However, emerging research indicates it might also be a viable option for women with female pattern baldness, offering a new perspective on hair loss treatment.
While traditionally seen as a male-targeted treatment due to concerns over side effects, the topical form of Finasteride presents a less systemic option, potentially widening its applicability.
This could be particularly beneficial for women, who are often advised against using oral Finasteride because of the risk of birth defects and hormonal imbalances
However, it's important to note that topical Finasteride is still under investigation and has not been officially licensed for use in treating hair loss in either men or women as of my last update. Its safety and efficacy, while promising, are still subjects of ongoing research.
How long does topical Finasteride take to work?

Topical Finasteride typically begins to show results, such as a visible reduction in hair loss, within six months of consistent use. This timeline is somewhat longer compared to the oral form of the medication, which may produce noticeable effects as early as four months.
The effectiveness and the time it takes to see results can vary widely among individuals. Factors such as the pattern and stage of hair loss, the concentration of the topical solution, and how consistently it's applied all play significant roles
For some, significant improvements may take up to a year or more, especially when looking for hair regrowth in areas that were previously thinning.
It's equally vital for individuals undergoing topical Finasteride or topical Minoxidil treatment to adhere to a consistent application routine to maximize male pattern hair loss, growth and treatment efficacy for male pattern hair loss.
A better alternative to topical Finasteride for your hair
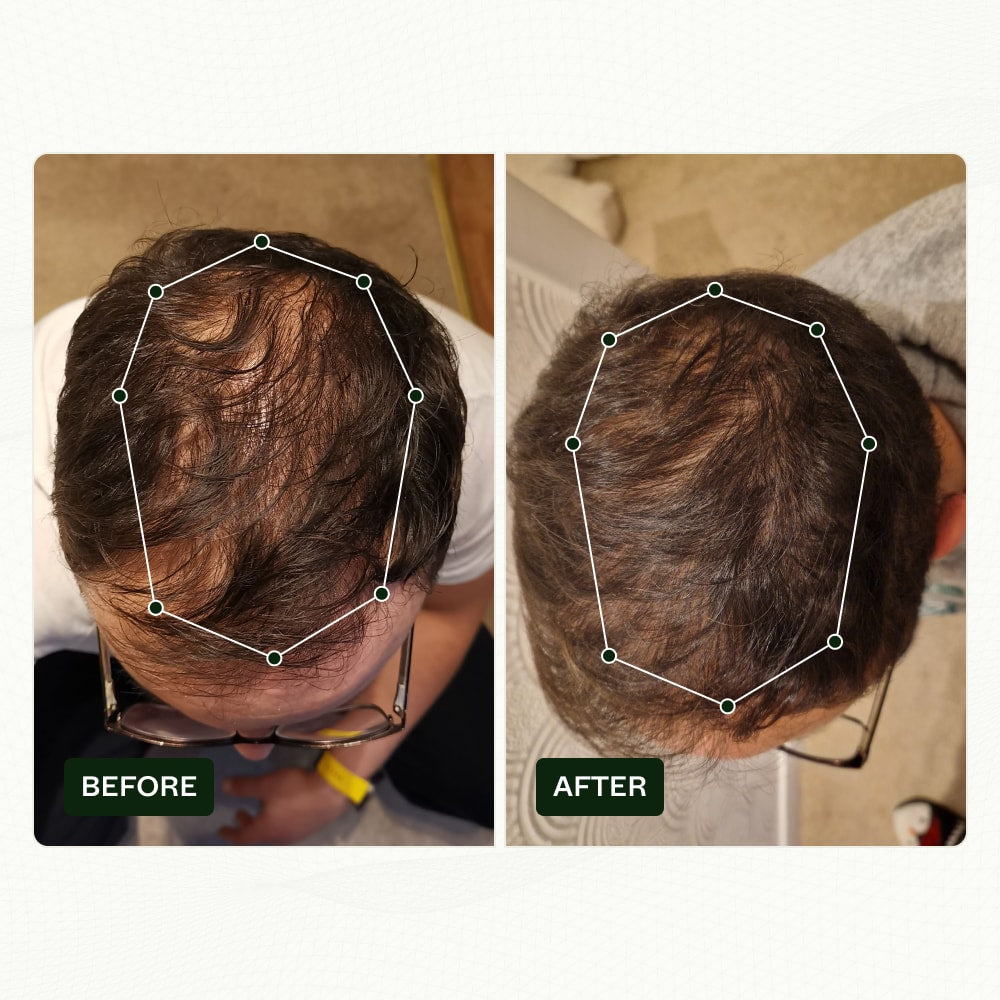
Bio-Pilixin Serum stands out as a notable alternative to topical Finasteride for those exploring hair loss solutions.
This expertly developed serum is aimed not just at reducing hair loss but also at encouraging new hair regrowth, making it an innovative hair loss treatment that leverages plant growth factors derived from stem cell technology to treat hair loss effectively.
Clinically tested to show results in as little as 45 days, Bio-Pilixin Serum offers a blend of high-quality, vegan ingredients
The formula includes Capilia Longa, a natural compound that has shown up to 89% reduction in hair loss and a 52% improvement in hair density in studies.
Niacinamide is another key ingredient, known for its role in stimulating keratin production, thereby contributing to stronger, healthier hair
Furthermore, the serum contains Vanillyl Butyl Ether, a mild warming agent that improves blood circulation to the scalp, enhancing nutrient and oxygen delivery to the hair follicles
With its nature-inspired and scientifically supported formula, Bio-Pilixin Serum represents a holistic approach to combating hair loss, emphasizing scalp nourishment and the natural hair growth process.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of hair loss treatments can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options, from topical Finasteride to innovative alternatives like Bio-Pilixin Serum from Scandinavian Biolabs, can empower you to make choices that best suit your needs and lifestyle.
While topical Finasteride offers a less systematic approach compared to its oral counterpart, potential side effects and considerations still warrant a careful decision-making process.
For those seeking a more natural route, Bio-Pilixin Serum presents a compelling alternative. Its blend of scientifically backed, vegan ingredients aims to reduce hair loss and support hair growth with minimal side effects, backed by promising clinical trials results.
As you weigh your options, remember that the path to restoring your hair may require patience and persistence.
Whether you opt for a topical treatment of Finasteride or decide to explore the benefits of Bio-Pilixin Serum, staying informed and proactive is key to navigating your hair loss treatment successfully.
FAQs
What are the common side effects of topical Finasteride?
Mild side effects commonly associated with topical Finasteride include erythema, which is a superficial, localized redness of the skin, and contact dermatitis. These reactions are generally due to irritation of the skin where the medication is applied.
Can topical Finasteride cause more serious side effects?
Though less common, there have been reports of more serious side effects in some individuals using topical Finasteride, such as presyncope (a feeling of lightheadedness or nearly fainting), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye), headache, and oropharyngeal pain (pain in the throat or mouth).
Does using topical Finasteride affect testosterone levels?
Yes, Finasteride, including its topical form, can increase circulating levels of testosterone. This increase in testosterone is often converted peripherally to estrogens, which means that in older males, the use of oral Finasteride tablets might shift the hormonal balance towards an excess of estrogen.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34291720/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6609098/pdf/nihms-1035387.pdf
Read more:
- Does Prednisone Cause Hair Loss? Here's Everything You Need To Know
- 11 Best Hair Loss Shampoo Of 2024 In Hands-On Test
- Bangs For Thin Hair: 25 Best And Worst Ideas For Thinning Fringe To Try In 2024







